What Is the Bounce Rate Of A Website Or A Webpage?
Avinash Kaushik, an author of multiple books on digital marketing, came up with a famous definition of bounce rate in SEO. He says it’s like a user saying, “I came, I puked, I left.”
It is a metric that tells you about the percentage of people who land on your website and do not reach the end goals you want, such as making a purchase, reading a blog, watching a video and so on. These users do not even click on a menu item in the navigation, a “read more” link or any other internal links on the page. Such visits are called single-page visits, with no engagement.
You can find in the “overview” report under the “audience” section on your Google Analytics dashboard. The bounce rate in Google Analytics is quite reliable and can help understand the behavior of users.
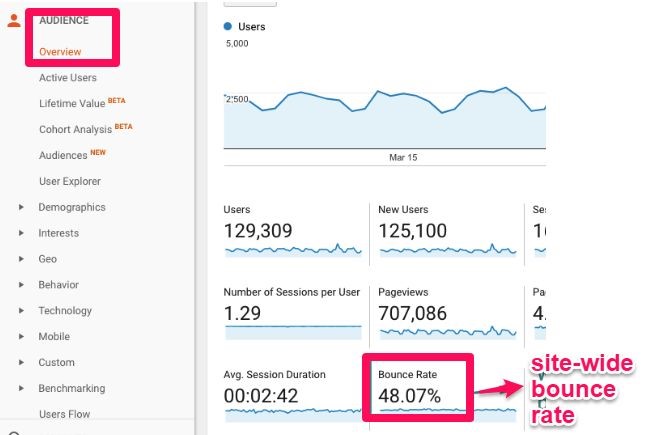
Source: Neil Patel
A bounce rate defines the quality of your webpage and the quality of your audience. Does your webpage fulfill the purpose of the reason the audience visited the website for?
How Is A Bounce Rate Calculated?
According to Google Analytics, the bounce rate in SEO is calculated by:
“Bounce rate is the percentage of all sessions on your website, of which users have only viewed a single page and triggered only a single request to the analytics server”.
In simpler words, the bounce rate of a website is the number of sessions where users visited only one page divided by all sessions.
A higher bounce rate results in providers believing that your content is spam and it redirects from the inbox to the junk or blocks them.
What Is The Average Bounce Rate Of Websites?
An optimal bounce rate depends on industry to industry. Optimal bounce rates for various industries are:
- 20% – 40% for retail websites
- 70% – 90% for simple landing pages with one call to action
- 10% – 30% for portals
- 25% – 55% for B2B websites
- 10% – 30% for service websites, including self-service websites and FAQ websites
- 40% – 60% for content websites
- 30% – 50% for lead generation websites
However, on average, an optimal bounce rate is somewhere between 25% to 40%. You might fall in the mean if the bounce rate is between 41% and 55%. What can be alarming is, is a bounce rate between 56% to 70%. You should troubleshoot for problems and fix them.
What Is The Difference Between Bounce Rate And Exit Rate?
Bounce rate is commonly misunderstood as exit rate. The exit rate is the percentage of last page views in the session. Google calculates exit rates and bounce rates as:
Day 1: Page B > Page A > Page C > Exit
Day 2: Page B > Exit
Day 3: Page A > Page C > Page B > Exit
Day 4: Page C > Exit
Day 5: Page B > Page C > Page A > Exit
The % Exit and Bounce Rate calculations are:
Exit Rate of each page:
A: 33% (3 sessions included Page A, 1 session exited from Page A; 1/3)
B: 50% (4 sessions included Page B, 2 sessions exited from Page B; 2/4)
C: 50% (4 sessions included Page C, 2 sessions exited from Page C; 2/4)
Bounce Rate of each page:
A: 0% (one session began with Page A, but that was not a single-page session, so it has no Bounce Rate)
B: 33% (Bounce Rate is less than Exit Rate because 3 sessions started with Page B, with one leading to a bounce; 1/3)
C: 100% (one session started with Page C, and it lead to a bounce; 1/1)
Reasons Behind High Bounce Rate of Websites
There could be various reasons of a bounce rate, and in an ideal world, you could ask all the users their reason for bouncing off in an interview. Studies have, however, suggested that there are a few common reasons for users to bounce off a webpage.
Low Page Quality
A page with low quality has nothing for users to engage with, such as no videos, internal links, a confusing menu, no search bar, no blogs with graphical content and so on.
Expectations of Users are Not Fulfilled
Users enter a page with some expectations. If they have clicked on a social media ad about a product on sale, they expect to see the same image upon landing and a similar price with the item on discount. If the product image or color is different, sizes are unavailable or the updated price isn’t mentioned, the user is likely to close the webpage, increasing the bounce rate.
Do not lure your visitors under false pretenses. Otherwise, they will close your webpage resulting in a higher bounce rate.
Unattractive Design
People generally judge your website based on the first impression they get by looking at the design. Use attractive colors that relate to your industry, and keep a consistent theme and branding throughout.
When Can A Higher Bounce Rate Be A Good Sign?
To interpret bounce rate metrics, you should keep in mind the goals of your website. If the success of your website depends on viewing multiple pages, such as browsing through different products and making a purchase, a high bounce rate is bad.
If your website is a single-page site or offers content like blogs, news or videos, then it is expected that the user will exit once the content is consumed. Hence, a high bounce rate is perfectly normal, in fact healthier for your digital service.
How To Improve Bounce Rate and Make More Conversions?
If you look at bounce rate from the perspective of making a conversion, then the metric can be used to measure success. The more people bounce off your website, the lesser the likelihood of conversions.
Segment your bounce rate analysis by multiple factors.
One of those factors could be age. A high bounce rate for users aged 65+ may not be a worry because people aged 65 or more is not your target market.
Another factor is gender. It could explain which sect of the population you should be targeting and campaigning for and whether you’re completely isolating the other genders.
Location is another important factor that could be considered. If your eCommerce website does not ship to Asia, there will definitely be a higher bounce rate for Asian countries as compared to European countries.
Other factors could include web browsers, devices, traffic source or acquisition, new vs returning users, etc.
Try to Understand Users’ Intentions
More content isn’t always the best tactic. Sometimes, you need to find the sweet spot and understand the behavior of users and what they are looking for. Focus on the quality of your users and not the quantity.
Design For Better User Experience
To design for a better user experience, understand the users’ pain points. The first moment of frustration for a user is when the website takes longer than usual to load.
If the loading speed is from 1-3 seconds, the probability of bounce increases by 32%. If it goes on to 5 seconds, the bounce rate increases to 90%. As a result, avoid using heavy images and videos that slow down the website speed.

Source: SearchENgineLand
Saving some bucks on your hosting provider’s service can turn out really costly if users start leaving your website at a slow speed.
Track The Source of Traffic
Understand where a higher bounce rate is coming from.
Is it your newsletter? You should change your newsletter content in that case.
Is it your social media ads? Are you showing the same image in your ads and on your landing page?
Is it your Google Search results? Are your meta descriptions correctly describing your pages?
Data from traffic sources is available on your Google Analytics dashboard and can be interpreted easily.
Check The Readability Of Your Text
A webpage should have enough white spaces for people to scan or read the text. Use larger font sizes and multiple subheadings to avoid big chunks of text, add bullet points to make important information easy to find, and write shorter paragraphs that are easier to skim through. Additionally, include images, infographics, and charts to convey complicated information in an easy manner.

Source: Neil Patel
Provide Relevant Information Above The Fold of the Page
People decide to stay on the page or leave based on what they see “above the fold”, that is, the top half of the page. To ensure a lower bounce rate, write an introduction that keeps the user glued to the content.
Follow the PPT template to grab your users’ interest.
P: Promise
P: Proof
T: Transition
Tell them about the promise that you will deliver to them and credibly build up on it with proof. Finally, end with a transition that encourages them to scroll down.
Add Relevant Internal Links
Being an integral part of your SEO Strategy, internal links lead a visitor to other pages on your website; hence they are excellent for improving your bounce rate. It naturally gives pageviews. However, the links shouldn’t be stuffed into the face of the user but be linked naturally for users to find helpful content for themselves.
Follow The Mobile First Principle
As a general practice, people are now using mobile phones to view websites and consume content. Consequently, Google is now prioritizing mobile experience, and websites with a webpage optimized for mobiles rank higher.
Add Clear Call To Action Buttons
Design your website according to the goals you have for the user. If you want the user to sign up for your newsletter, have a clear call-to-action button that stands out from the rest of the page; it should catch the user’s attention.
Having multiple call-to-action buttons can frustrate the user and confuse them. This is why you always A/B test your call-to-action buttons.
Use Heatmap Data to Improve Landing Pages
Heatmaps are a great way to understand how users interact with your website. You can add a chunk of javascript to your website and it helps you track how people read, click and scroll around your page. If people do not focus on a certain element of your website, it is better to remove it altogether.
How Does A High Bounce Rate Affect SEO of a Website?
An SEO strategy is incomplete without considering the bounce rate since it is an important metric to measure the website’s health. If a user clicks your website from a search engine result page and leaves without interaction, it communicates to Google that this kind of content isn’t what the user is looking for. As a result, Google pushes down the ranking of the page.
What Is An Email Bounce Rate?
The email bounce rate is slightly different than the website bounce rate. Email bounce rate refers to the number of emails sent to recipients that could not be delivered to their inboxes successfully.
If you have a high bounce rate, your emails can go undelivered to your audience, resulting in lost leads and unsuccessful conversions. Bounce rate can be of two types: hard bounces and soft bounces.
Hard bounces are emails that are sent back by the email provider because of incorrect addresses, incorrect domains and so on. A soft bounce is a bounce after the email provider accepts it, such as when the recipient’s inbox is full or the email is too large.
To calculate email bounce rate:
Email Bounce Rate = (Number of Bounces / Number of Delivered Emails) X 100
What Is An Average Email Bounce Rate?
An average email hard bounce rate is 0.4%, whereas a soft bounce rate is 0.58%. It varies across industries, but generally, you should aim to have a bounce rate of 2% or lower.
Final Thoughts
Bounce Rate is not a very tricky metric to tackle. Analyze and interpret it and confirm your findings through heatmaps or user interviews to understand your visitor’s behavior. Improving the website’s bounce rate can be effective in driving conversions. Be consistent in your efforts and see the results!

